Incoterms® 2020
What are Incoterms?
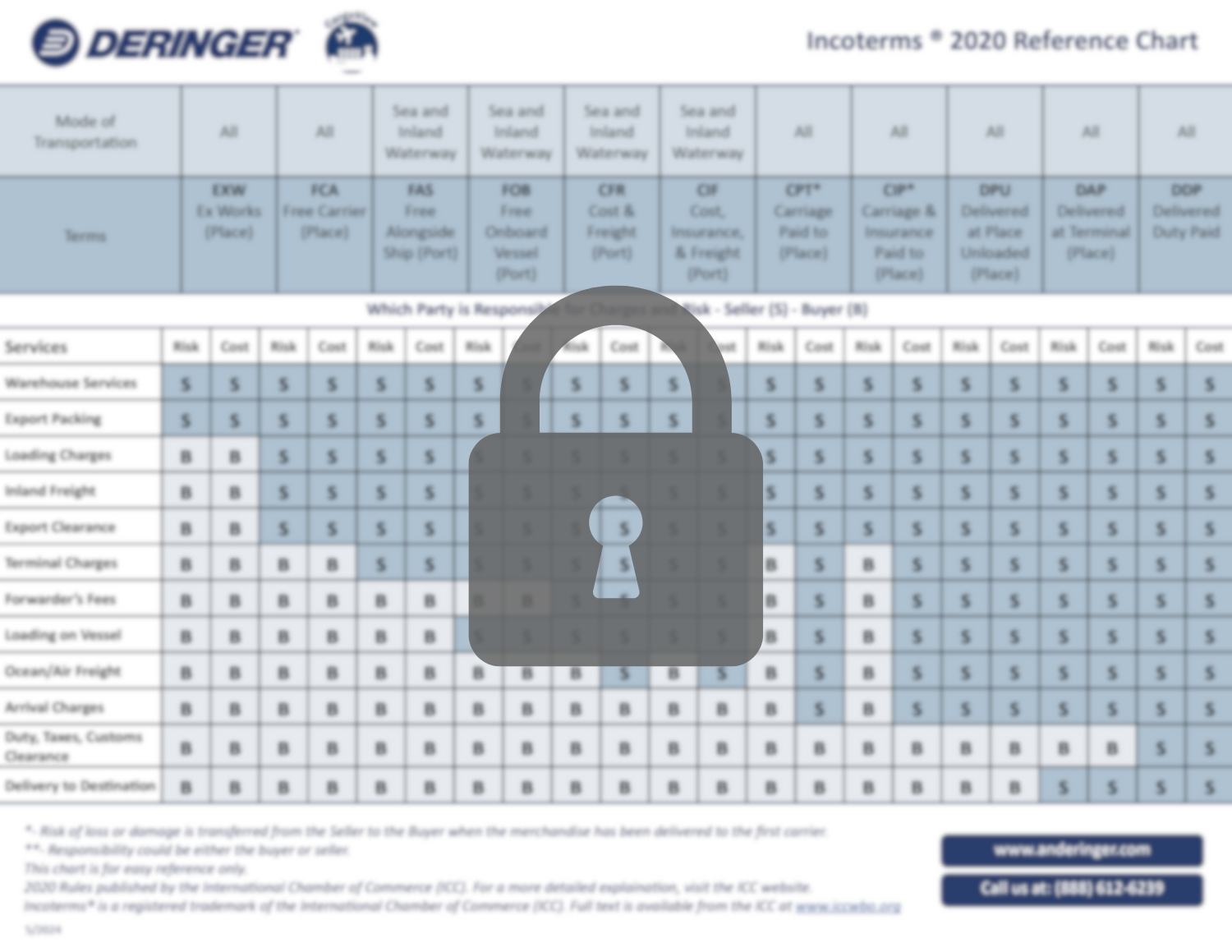
Incoterms®, short for international commercial terms, are a set of globally recognized rules that define responsibilities, costs, and risks in global trade. The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) publishes a new set of Incoterms every 10 years, with the most recent set releasing in 2020. Here is a breakdown of the 11 Incoterms:
-
Ex Works (EXW). Ex Works, assigns minimal responsibility to the seller, whose key role is to package and deliver goods to a designated location. From there, the buyer handles loading goods, export procedures, and pays all shipping costs incurred.
-
FCA (Free Carrier). The most popular Incoterm, used in 40% of international trade operations. Allows you to note the delivery destination of goods, whether it is a port, an airport, a container freight station, or the seller’s address.
-
FAS (Free Alongside Ship). Implies that the seller has delivered the shipment once they place it alongside the pre-established vessel.
-
FOB (Free on Board). The seller must deliver goods on board the vessel of the buyer’s choosing at their named port. The responsibility for loss or damage transfers from seller to buyer once goods get loaded on a vessel.
-
CFR (Cost and Freight). The seller is responsible for placing the goods on board the vessel and paying all transport costs to the point of destination. Once the goods are on board, the responsibility shifts to the buyer.
-
CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight). CIF works in the same way as CFR with one key difference: the seller is required to purchase at least minimum coverage marine cargo insurance.
-
CPT (Carriage Paid To). The seller pays carriage costs to a destination agreed upon by both parties.
-
CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To). The seller pays freight and insurance until delivery to the first carrier. When the carrier assumes control, the buyer takes on all risks, but the seller must cover carriage costs and provide all-risk insurance until freight reaches its destination.
-
DAP (Delivered at Place). The seller assumes all responsibilities until the goods are delivered and available to the buyer at the designated location.
-
DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded). This Incoterm replaced DAT (Delivered at Terminal) in 2020. The seller assumes all responsibilities and risks until the goods are unloaded and available to the buyer at the designated location. This is the only Incoterm that requires the seller to unload the goods at the destination. The buyer is responsible for the delivery to the destination and import duties and taxes.
-
DDP (Delivery Duty Paid). The seller bears all responsibility for the cost of the shipment, duty included.
How to Expand Your Incoterms Knowledge:
Listen to Brief Incoterms Summaries
Our podcast, Time Out for Trade, is actively posting new episodes about each of the Incoterms. You can listen to subject matter experts explaining each Incoterm, with each episode only being a few minutes long.